Aortic dissection in Siriraj patients: Computed tomography findings
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46475/aseanjr.v19i3.10Keywords:
Aortic dissection, Stanford classification, Computed Tomography angiography, Siriraj patientsAbstract
Background: CTA has replaced angiography in both diagnosis and evaluation of aortic dissection. Most findings are associated with true and false lumens which account for the most important information in both diagnosis and management.
Objective: To describe computed tomographic (CT) findings including types based on Stanford classification, true and false lumens, acute and chronic aortic dissections, relation to origins of aortic branches, complications and other related findings.
Methods: Computed tomographic angiography (CTA) scans of one hundred and twenty patients with aortic dissection during 2007 to 2016 were retrospectively reviewed. The findings indicating types, true and false lumens, acute and chronic, origination of aortic branches, complication and other related findings are categorized.
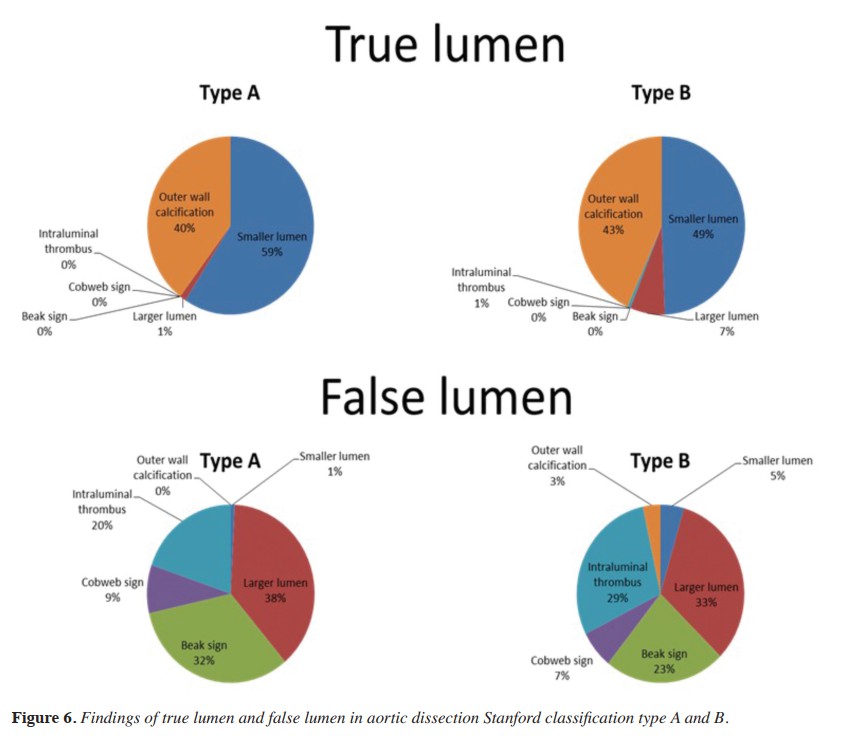
Result: Most true lumens were smaller, having outer wall calcification. Most false lumens were larger, showing beak sign, cobweb sign, and intraluminal thrombi. However, the larger lumens could be true lumens as well as the smaller lumen could be a false lumen and outer wall calcification could be seen in a false lumen. The larger true lumens and the smaller false lumens with outer wall calcifications were more often found in chronic aortic dissection than acute aortic dissection. Both acute and chronic aortic dissections were more Stanford type B than type A. Complications included rupture, hemopericardium, hemothorax, hemomediastinum and distal organ infarction, which were more frequent in acute dissection. Intrathoracic complications were more commonly caused by type A acute dissection. Renal infarction was the most common complication in type B acute aortic dissection.
Conclusion: Most CT fi ndings of aortic dissection in this study were typical. Atypical fi ndings were also found in both acute and chronic aortic dissections. Outer wall calcifi cations of false lumens in acute aortic dissection were found in 2 cases.
Downloads
Metrics
References
LePage MA, Quint LE, Sonnad SS, Deeb GM, Williams DM. Aortic dissection: CT features that distinguish true lumen from false lumen. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001;177:207-11.
Kapoor V, Ferris JV, Fuhrman CR. Intimomedial rupture: a new CT finding to distinguish true from false lumen in aortic dissection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004;183:109-12.
Fisher ER, Stern EJ, Godwin JD 2nd, Otto CM, Johnson JA. Acute aortic dissection: typical and atypical imaging features. Radiographics 1994;14:1263-71; discussion 1271-4.
Blount KJ, Hagspiel KD. Aortic diameter, true lumen, and false lumen growth rates in chronic type B aortic dissection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009; 192:W222-9.
McMahon MA, Squirrell CA. Multidetector CT of Aortic Dissection: A Pictorial Review. Radiographics 2010;30:445-60.
Castañer E, Andreu M, Gallardo X, Mata JM, Cabezuelo MA, Pallardó Y. CT innontraumatic acute thoracic aortic disease: typical and atypical features and complications. Radiographics 2003;23 Spec No:S93-110.
Burrill J, Dabbagh Z, Gollub F, Hamady M. Multidetector computed tomographic angiography of the cardiovascular system. Postgrad Med J 2007;83:698-704.
Steuer J, Björck M, Mayer D, Wanhainen A, Pfammatter T, Lachat M. Distinction between acute and chronic type B aortic dissection: is there a sub-acute phase? Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2013;45:627-31.
Loftus IM, Thompson MM. Commentary on 'distinction between acute and chronic type B aortic dissection: is there a subacute phase?'. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2013;45:632.
Augoustides JG, Szeto WY, Desai ND, Pochettino A, Cheung AT, Savino JS, et al. Classification of acute type A dissection: focus on clinical presentation and extent. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2011;39:519-22.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2017 The ASEAN Journal of Radiology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Disclosure Forms and Copyright Agreements
All authors listed on the manuscript must complete both the electronic copyright agreement. (in the case of acceptance)
















