Associated ultrasound findings improve the accuracy of twinkling artifacts in kidney stone diagnosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46475/aseanjr.v23i3.189Keywords:
Twinkling artifact, Color doppler ultrasound, Kidney stones, Renal calculiAbstract
Background: Twinkling artifact (TA) in color Doppler ultrasound is commonly used as a sign of kidney tract stone detection but the accuracy is limited as compared with unenhanced computed tomography (CT).
Objective: Define the associated ultrasound findings that may improve the accuracy of TA compared with CT for diagnosing kidney stones.
Materials and Methods: Prospective study was conducted on 128 TAs in patients sent for unenhanced CT KUB and performed color Doppler ultrasound on the same day. TA sizes and associated sonographic signs were recorded and analyzed with receiver operating characteristic curves (ROCs). The diagnostic reference was the CT scan.
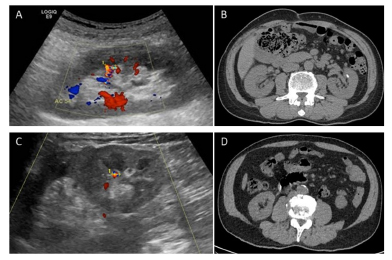
Results: There was a total of 128 TAs with the size of 3.95 mm (2.7-6 mm). Only 30 TAs showed as kidney stones in CT. The sizes of kidney stones in CT were 5.4 mm (3.4-6.4 mm) which represented a significant difference in TA size (P = 0.002). ROC curve analysis showed that 5 mm would be the optimal size of TA for kidney stone predictions. Other significant signs for improved diagnosis include echoic foci (P = 0.039), posterior shadows (P = 0.001), long TA tails (P = 0.001) and 2nd approach TA (P = 0.001). Then a predictive AT model was created to predict kidney stones, which moderately improved diagnosis accuracy for kidney stones with good agreement.
Conclusion: The combination of TA and other sonographic signs are moderately associated with kidney stone diagnosis including TA size (> 5 mm), posterior acoustic shadow, long TA tail, junctional line location and focal Caliectasis.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Bultitude M, Rees J. Management of renal colic. BMJ 2012;345:e5499. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e5499.
Korkmaz M, Aras B, Sanal B, Yucel M, Guneyli S, Kocak A, et al. Investigating the clinical significance of twinkling artifacts in patients with urolithiasis smaller than 5 mm. Jpn J Radiol 2014;32:482-6. doi: 10.1007/s11604-014-0337-6.
Ferrandino MN, Bagrodia A, Pierre SA, Scales CD Jr, Rampersaud E, Pearle MS, et al. Radiation exposure in the acute and short-term management of urolithiasis at 2 academic centers. J Urol 2009;181:668-72; discussion 73. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.10.012.
Rahmouni A, Bargoin R, Herment A, Bargoin N, Vasile N. Color Doppler twinkling artifact in hyperechoic regions. Radiology 1996;199:269-71. doi: 10.1148/radiology.199.1.8633158.
Aytac SK, Ozcan H. Effect of color Doppler system on the twinkling sign associated with urinary tract calculi. J Clin Ultrasound 1999;27:433-9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0096(199910)27:8<433::aid-jcu4>3.0.co;2-1.
Lee JY, Kim SH, Cho JY, Han D. Color and power Doppler twinkling artifacts from urinary stones: clinical observations and phantom studies. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001;176:1441-5. doi: 10.2214/ajr.176.6.1761441.
Logias F, Manca EM, Carta P, Granata A, Barracca A, Manca O. [Twinkling artifact in kidney stone disease]. G Ital Nefrol 2005;22:503-7. Italian.
Hanafi MQ, Fakhrizadeh A, Jaafaezadeh E. An investigation into the clinical accuracy of twinkling artifacts in patients with urolithiasis smaller than 5 mm in comparison with computed tomography scanning. J Family Med Prim Care 2019;8:401-6. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_300_18.
Masch WR, Cohan RH, Ellis JH, Dillman JR, Rubin JM, Davenport MS. Clinical Effectiveness of Prospectively Reported Sonographic Twinkling Artifact for the Diagnosis of Renal Calculus in Patients Without Known Urolithiasis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2016;206:326-31. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.14998.
Winkel RR, Kalhauge A, Fredfeldt KE. The usefulness of ultrasound colour-Doppler twinkling artefact for detecting urolithiasis compared with low dose nonenhanced computerized tomography. Ultrasound Med Biol 2012;38:1180-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2012.03.003.
Yavuz A, Ceken K, Alimoglu E, Kabaalioglu A. The reliability of color doppler "twinkling" artifact for diagnosing millimetrical nephrolithiasis: comparison with B-Mode US and CT scanning results. J Med Ultrason (2001) 2015;42:215-22. doi: 10.1007/s10396-014-0599-8.
Masch WR, Cronin KC, Sahani DV, Kambadakone A. Imaging in Urolithiasis. Radiol Clin North Am 2017;55:209-24. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2016.10.002.
Kielar AZ, Shabana W, Vakili M, Rubin J. Prospective evaluation of Doppler sonography to detect the twinkling artifact versus unenhanced computed tomography for identifying urinary tract calculi. J Ultrasound Med 2012;31:1619-25. doi: 10.7863/jum.2012.31.10.1619.
Kamaya A, Tuthill T, Rubin JM. Twinkling artifact on color Doppler sonography: dependence on machine parameters and underlying cause. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003;180:215-22. doi: 10.2214/ajr.180.1.1800215.
Bacha R, Manzoor I, Gilani SA, Khan AI. Clinical Significance of Twinkling Artifact in the Diagnosis of Urinary Stones. Ultrasound Med Biol 2019;45:3199-206. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.08.015.
Dillman JR, Kappil M, Weadock WJ, Rubin JM, Platt JF, DiPietro MA, et al. Sonographic twinkling artifact for renal calculus detection: correlation with CT. Radiology 2011;259:911-6. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11102128.
Laher AE, McDowall J, Gerber L, Aigbodion SJ, Enyuma COA, Buchanan S, et al. The ultrasound 'twinkling artefact' in the diagnosis of urolithiasis: hocus or valuable point-of-care-ultrasound? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Emerg Med 2019;27:13-20. doi: 10.1097/MEJ.0000000000000601.
Louvet A. Twinkling artifact in small animal color-Doppler sonography. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 2006;47:384-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1740-8261.2006.00158.x.
Sen V, Imamoglu C, Kucukturkmen I, Degirmenci T, Bozkurt IH, Yonguc T, et al. Can Doppler ultrasonography twinkling artifact be used as an alternative imaging modality to non-contrast-enhanced computed tomography in patients with ureteral stones? A prospective clinical study. Urolithiasis 2017;45:215-9. doi: 10.1007/s00240-016-0891-8.
Simon JC, Holm JR, Thiel J, Dunmire B, Cunitz BW, Bailey MR. Evidence of microbubbles on kidney stones in humans. Ultrasound Med Biol 2020;46:1802-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.02.010.
Kim HC, Yang DM, Jin W, Ryu JK, Shin HC. Color Doppler twinkling artifacts in various conditions during abdominal and pelvic sonography. J Ultrasound Med 2010;29:621-32. doi: 10.7863/jum.2010.29.4.621.
Lu W, Sapozhnikov OA, Bailey MR, Kaczkowski PJ, Crum LA. Evidence for trapped surface bubbles as the cause for the twinkling artifact in ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol 2013;39:1026-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2013.01.011.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 The ASEAN Journal of Radiology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Disclosure Forms and Copyright Agreements
All authors listed on the manuscript must complete both the electronic copyright agreement. (in the case of acceptance)
















