Abdominal CT radiation dose optimization at Siriraj Hospital
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46475/aseanjr.v21i2.80Keywords:
Abdominal computed tomography, Abdominal CT, Radiation dose reduction, Iterative reconstruction, IR, Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction, ASiRAbstract
OBJECTIVE: To compare radiation dose and image quality between standard dose abdominal CT currently performed at our hospital and new low dose abdominal CT using various percentages (0%, 10%, 20%, and 30%) of Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction (ASiR).
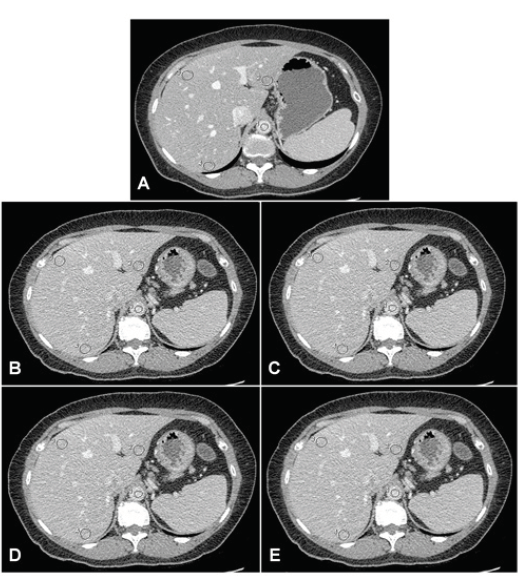
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We prospectively performed low dose abdominal CT (30% reduction of standard tube current) in 119 participants. The low dose CT images were post processed with four parameters (0%, 10%, 20% and 30%) of ASiR. The volume CT dose index (CTDIvol) of standard and low dose CT were compared. Four experienced abdominal radiologists independently assessed the quality of low dose CT with aforementioned ASiR parameters using a 5-point-scale satisfaction score (1 = unacceptable, 2 = poor, 3 = average, 4 = good, and 5 = excellent image quality) by using prior standard dose CT as a reference of excellent image quality (5). Each reader selected the preference ASiR parameter for each participant. The image noise of the liver and the aorta in all 5 (1 prior standard dose and 4 current low dose) image sets was measured.
RESULTS: The mean CTDIvol of low dose CT was significantly lower than of standard dose CT (7.17 ± 0.08 vs 12.02 ±1.61 mGy, p<0.001). The mean satisfaction scores for low dose CT with 0%, 10%, 20% and 30% ASiR were 3.95, 3.99, 3.91 and 3.87, respectively with the ranges of 3 to 5 in all techniques. The preferred ASiR parameters of each participant randomly selected by each reader were varied, depending on the readers’ opinions. The mean image noise of the aorta on standard dose CT and low dose CT with 0%, 10%, 20%, and 30% ASiR was 29.07, 36.97, 33.92, 31.49, and 29.11, respectively, while the mean image noise of the liver was 24.60, 30.21, 28.33, 26.25, and 24.32, respectively.
CONCLUSION: Low dose CT with 30% reduction of standard mA had acceptable image quality with significantly reduced radiation dose. The increment of ASiR was helpful in reducing image noise.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Hara AK, Wellnitz CV, Paden RG, Pavlicek W, Sahani DV. Reducing body CT radiation dose: beyond just changing the numbers. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013;201:33-40. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.13.10556.
Tamm EP, Rong XJ, Cody DD, Ernst RD, Fitzgerald NE, Kundra V. Quality initiatives: CT radiation dose reduction: how to implement change without sacrificing diagnostic quality. RadioGraphics 2011;31:1823-32. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.317115027.
Patino M, Fuentes JM, Singh S, Hahn PF, Sahani DV. Iterative reconstruction techniques in abdominopelvic CT: technical concepts and clinical implementation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2015;205:W19-31. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.14.13402.
Willemink MJ, de Jong PA, Leiner T, de Heer LM, Nievelstein RA, Budde RP, et al. Iterative reconstruction techniques for computed tomography Part 1: technical principles. Eur Radiol 2013;23:1623-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2765-y.
Higaki T, Nakamura Y, Fukumoto W, Honda Y, Tatsugami F, Awai K. Clinical application of radiation dose reduction at abdominal CT. Eur J Radiol 2019;111:68-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.12.018.
Mitsumori LM, Shuman WP, Busey JM, Kolokythas O, Koprowicz KM. Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction versus filtered back projection in the same patient: 64 channel liver CT image quality and patient radiation dose. Eur Radiol 2012;22:138-43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2186-3.
Chang W, Lee JM, Lee K, Yoon JH, Yu MH, Han JK, et al. Assessment of a model-based, iterative reconstruction algorithm (MBIR) regarding image quality and dose reduction in liver computed tomography. Invest Radiol 2013;48:598-606. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182899104.
Singh S, Kalra MK, Gilman MD, Hsieh J, Pien HH, Digumarthy SR, et al. Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique for radiation dose reduction in chest CT: a pilot study. Radiology 2011;259:565-73. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.11101450.
Gervaise A, Osemont B, Louis M, Lecocq S, Teixeira P, Blum A. Standard dose versus low-dose abdominal and pelvic CT: comparison between filtered back projection versus adaptive iterative dose reduction 3D. Diagn Interv Imaging 2014;95:47-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2013.05.005.
Singh S, Kalra MK, Hsieh J, Licato PE, Do S, Pien HH, et al. Abdominal CT: comparison of adaptive statistical iterative and filtered back projection reconstruction techniques. Radiology 2010;257:373-83. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10092212.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 The ASEAN Journal of Radiology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Disclosure Forms and Copyright Agreements
All authors listed on the manuscript must complete both the electronic copyright agreement. (in the case of acceptance)
















